Dr. Cihan Bacaksiz

| Fields of interest | 2D magnetic materials and spin dynamics |
| Publications | Google Scholar |
Research
My researches focus on density functional theory based understanding of magnetic properties, isotropic and anisotropic magnetic exchange interactions in two-dimensional materials, multilayers, and non-collinear spin systems. On top of that the classical Monte-Carlo simulation based on Ising and Heisenberg spin Hamiltonian are also in my research scope which allow me to study the temperature-dependent magnetic properties of magnetic materials, magnetic phase transitions, and non-trivial spin-textures. In addition, I study density functional theory based investigation of the electronic, optical and vibrational properties of two-dimensional materials; adsorption and substitutions of atoms, surface properties, strain engineering of physical properties as well as the temperature-dependent stability analyses of material by using ab initio molecular dynamic simulations.
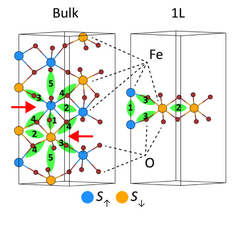
Thinned down from hematite to hematene: an AFM two-dimensional iron oxide
Motivated by the recent synthesis of two-dimensional -Fe2O3 (Balan et al 2018 Nat. Nanotechnol. 13 602), we analyze the structural, vibrational, electronic and magnetic properties of single- and few-layer -Fe2O3 compared to bulk, by ab initio and Monte-Carlo simulations. We reveal how monolayer -Fe2O3 (hematene) can be distinguished from the few-layer structures, and how they all differ from bulk through observable Raman spectra. The optical spectra exhibit gradual shift of the prominent peak to higher energy, as well as additional features at lower energy when -Fe2O3 is thinned down to a monolayer. Both optical and electronic properties have strong spin asymmetry, meaning that lower-energy optical and electronic activities are allowed for the single-spin state. Finally, our considerations of magnetic properties reveal that 2D hematite has anti-ferromagnetic ground state for all thicknesses, but the critical temperature for Morin transition increases with decreasing sample thickness. On all accounts, the link to available experimental data is made, and further measurements are prompted.
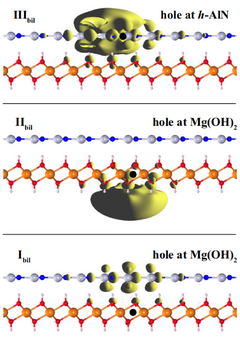
Theoretical prediction of Inter- and intralayer excitons in h-AlN /Mg(OH)2
Motivated by recent studies that reported the successful synthesis of monolayer Mg(OH)2 [Suslu et al., Sci. Rep. 6, 20525 (2016)] and hexagonal (h−)AlN [Tsipas et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 251605 (2013)], we investigate structural, electronic, and optical properties of vertically stacked h-AlN and Mg(OH)2, through ab initio density-functional theory (DFT), many-body quasiparticle calculations within the GW approximation and the Bethe-Salpeter equation (BSE). It is obtained that the bilayer heterostructure prefers the AB′ stacking having direct band gap at the Γ with Type-II band alignment in which the valance band maximum and conduction band minimum originate from different layer. Regarding the optical properties, the imaginary part of the dielectric function of the individual layers and heterobilayer are investigated. The heterobilayer possesses excitonic peaks, which appear only after the construction of the heterobilayer. The lowest three exciton peaks are analyzed in detail by means of band decomposed charge density and the oscillator strength. Furthermore, the wave function calculation shows that the first peak of the heterobilayer originates from spatially indirect exciton where the electron and hole localized at h-AlN and Mg(OH)2, respectively, which is important for the light harvesting applications.
